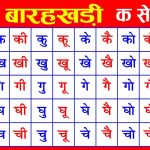
Marathi, a rich and expressive language, offers numerous avenues for developing writing skills.
Today we will help you to sharp your marathi writing skills, including essay writing, letter writing, poetry, story writing, advertising, news writing, dialogue writing, and additional skills such as translation and summarization. Additionally, it provides tips for finding inspiration from various sources.
Basics of Marathi Script
Marathi is written in the Devanagari script, which is also used for Hindi, Sanskrit, and several other Indian languages. The script consists of 36 consonants and 16 vowels. Learning Marathi writing begins with mastering the बराखडी (Barakhadi), which shows various consonant-vowel combinations. For example:
- क (ka) + ा (aa) = का (kaa)
- च (cha) + ि (i) = चि (chi)
- त (ta) + े (e) = ते (te)
Grammar and Sentence Structure
Marathi grammar shares similarities with other Indo-Aryan languages. It includes aspects such as gender (masculine, feminine, neuter), number (singular, plural), and case (nominative, accusative, etc.). Sentences in Marathi follow a Subject-Object-Verb (SOV) order. For instance:
- राम आंबा खातो. (Ram mango eats.) translates to “Ram eats a mango.”
Common Phrases and Their Usage
Understanding common phrases helps in everyday communication as well as in formal writing:
- नमस्कार (Namaskar) – Hello
- कसा काय? (Kasa kay?) – How are you?
- धन्यवाद (Dhanyavad) – Thank you
Writing Formal and Informal Letters
The format for formal letters in Marathi is quite structured:
- Start with the sender’s address on the top right, followed by the date.
- The recipient’s address appears on the left.
- The letter opens with a formal greeting such as प्रिय महोदय (Priya Mahodaya – Dear Sir).
- Conclude with a formal closing such as आपला, (Aapla – Yours).
Informal letters can be more relaxed and begin with a personal greeting like प्रिय मित्रा (Priya Mitra – Dear friend).
Literary Devices
Marathi literature makes extensive use of literary devices such as:
- उपमा (Upama – Simile): त्याचा चेहरा चंद्रासारखा (His face is like the moon).
- रूपक (Roopak – Metaphor): तू शेर आहेस (You are a lion).
- अनुप्रास (Anupras – Alliteration): तिचे तितके तटस्थ तर्क (Her so neutral arguments).
Common Mistakes in Marathi Writing
Avoiding common mistakes can improve the clarity and effectiveness of writing:
- Mixing of न (na) and ण (ṇa), which are distinct sounds in Marathi.
- Incorrect use of gender-specific verb endings.
- Overuse of English loanwords in formal Marathi writing.
Other Marathi Writing Skills
Nibandh Lekhan (निबंध लेखन)
Nibandh Lekhan, or essay writing, is a significant component of Marathi writing skills. It encompasses different subcategories:
Varnanatmak Nibandh (वर्णनात्मक निबंध)
Descriptive essays focus on vividly describing places, seasons, nature, travel experiences, or events. The goal is to create a mental image for the reader, making them feel as if they are experiencing the subject firsthand.
Example:
- Topic: A Rainy Day in Mumbai
- Description: “As the first drops of rain touched the parched earth of Mumbai, the city transformed into a lush, vibrant landscape. The aroma of wet soil filled the air, and the rhythmic sound of raindrops created a soothing symphony…”
Kathanatmak Nibandh (कथनात्मक निबंध)
Narrative essays tell stories, which can be personal experiences or fictional tales.
Atmavrittatmak Nibandh (आत्मवृत्तात्मक निबंध)
Personal experience essays recount significant events in the writer’s life.
Example:
- Topic: My First Day at College
- Narrative: “Walking through the college gates for the first time, I felt a mixture of excitement and nervousness. The bustling campus, the new faces, and the prospect of a fresh academic journey…”
Kalpanatmak Nibandh (कल्पनात्मक निबंध)
Fictional stories explore imaginative scenarios.
Example:
- Topic: A Journey to Mars
- Narrative: “In the year 2050, I found myself aboard a spacecraft hurtling towards Mars. The red planet, with its mysterious landscapes and potential for new beginnings…”
Vichaarpradhan Nibandh (विचारप्रधान निबंध)
Argumentative essays present a viewpoint on a particular issue, supported by evidence and reasoning.
Example:
- Topic: The Importance of Renewable Energy
- Argument: “As the world faces the looming threat of climate change, the shift towards renewable energy sources like solar and wind power has become imperative…”
Patralekhan (पत्रलेखन)
Letter writing in Marathi can be categorized into formal and informal.
Formal Letters
These are used for official communication, such as job applications, complaint letters, or requests.
Example:
- To the Principal,
- Subject: Request for Extra Classes
- Body: “Respected Sir/Madam, I am writing to request additional classes for Mathematics to better prepare for the upcoming board exams…”
Informal Letters
These are written to friends, family, or acquaintances.
Example:
- Dear Friend,
- Body: “How have you been? I recently visited the beautiful beaches of Goa and thought of you. The serene environment reminded me of our childhood trips…”
Kavita Lekhan (कविता लेखन)
Poetry writing allows for creative expression through various forms and styles.
Example:
- Haiku:
- “Rain on leaves,
- Nature’s symphony sings,
- Life anew.”
Katha Lekhan (कथा लेखन)
Story writing involves crafting fictional narratives that captivate the reader.
Example:
- Title: The Enchanted Forest
- Story: “Deep in the heart of the ancient forest lay a hidden realm where trees whispered secrets and animals spoke. Young Arjun, an adventurous boy, stumbled upon this magical world…”
Jahirati Lekhan (जाहिरात लेखन)
Advertising writing focuses on creating persuasive and catchy ad copy.
Example:
- Product: Herbal Shampoo
- Ad Copy: “Experience the power of nature with our Herbal Shampoo. Made from the finest herbs, it revitalizes your hair, leaving it silky and strong. Try it today for a natural glow!”
Batmi Lekhan (बातमी लेखन)
News writing involves reporting factual events clearly and concisely.
Example:
- Headline: Local School Wins National Science Competition
- Report: “In an inspiring achievement, students from XYZ School won the national science competition held in Delhi. Their innovative project on renewable energy impressed the judges…”
Sanvad Lekhan (संवाद लेखन)
Dialogue writing develops conversations between characters, enhancing the narrative.
Example:
- Characters: Two friends
- Dialogue: “Rohit: Have you heard about the new café in town? Meera: Yes, I went there yesterday. The ambiance is amazing!”
Additional Skills
Bhashantar (भाषांतर)
Translation skills involve converting writing from another language to Marathi accurately and fluently.
Example:
- Original (English): “The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.”
- Translation (Marathi): “चपळ तपकिरी कोल्हा आळशी कुत्र्यावर उडी मारतो.”
Saransh Lekhan (सारांश लेखन)
Summarization skills help condense lengthy passages into concise summaries.
Example:
- Original Text: “The development of renewable energy sources is crucial in combating climate change…”
- Summary: “Renewable energy is vital for climate change mitigation.”
Finding Inspiration
Current Events
Write about social issues, technological advancements, or environmental concerns.
Marathi Literature
Read the works of famous Marathi authors and analyze their writing styles for inspiration.
Personal Experiences
Write about your hobbies, passions, or challenges you’ve faced.
Marathi Culture
Explore topics related to Marathi traditions, festivals, or historical figures.
Explaining Marathi Writing Skills in Short
Sentence Structure in Marathi
The typical Marathi sentence follows a Subject-Object-Verb order. Understanding this helps in forming correct sentences, such as “राम खेळतो” (Ram plays).
Vocabulary Building in Marathi
Expanding your vocabulary can make your Marathi richer. Start with everyday items and actions, and use them in sentences to improve your memory.
Writing Marathi Alphabets and Numbers
Learning to write Marathi alphabets, which include 12 vowels and 36 consonants, is crucial. Practice writing numbers too, as they are used frequently in daily life.
Common Phrases and Expressions in Marathi
Knowing common phrases like “कसा काय?” (How are you?) can make your Marathi more conversational and natural.
Marathi Orthography
This refers to the set rules of writing in Marathi, including how letters and symbols are used in written language.
Writing Simple Sentences in Marathi
Start with basic sentences and gradually introduce new vocabulary. For example, “मला चहा हवा आहे.” (I want tea.)
Constructing Complex Sentences
Combine simple sentences using conjunctions to form complex sentences, enhancing the depth of your communication.
Punctuation in Marathi
Marathi uses punctuation marks similar to English, but their usage can differ, especially with the use of the full stop (।) known as ‘पूर्णविराम’.
Formal and Informal Writing Styles
Understand the difference between formal writing, used in official documents and reports, and informal writing, used in personal letters or messages.
Letter Writing in Marathi
Letters in Marathi follow a format that includes place, date, salutation, body, complimentary close, and signature.
Essay Writing in Marathi
Essays require a clear introduction, a body that discusses points in detail, and a concise conclusion.
Writing Reports in Marathi
Reports are factual and need clarity and conciseness, focusing on presenting information systematically.
Creative Writing in Marathi
Explore expressing thoughts imaginatively in poems, stories, and plays, paying attention to mood, setting, and characters.
Writing Poetry in Marathi
Poetry in Marathi can range from rhyming verses to free verse, focusing on emotions and experiences.
Writing Short Stories in Marathi
Short stories involve characters, a plot, and a setting, conveyed succinctly but vividly.
Translation Techniques: English to Marathi
Effective translation requires understanding the context and the nuances of both languages to maintain the original meaning.
Writing Dialogues in Marathi
Dialogues in plays or novels should sound natural and convey the characters’ emotions and intentions.
Writing Scripts for Plays and Dramas
Scripts require directions and dialogues that convey the story visually and verbally to the audience.
Writing Articles for Newspapers and Magazines
Articles should be engaging, well-researched, and tailored to the interests of the readership.
Writing Official Documents and Applications
Focus on clarity and formality, ensuring all required information is presented clearly and respectfully.
Writing Speeches in Marathi
Speeches need a strong opening, a persuasive body, and a memorable conclusion, tailored to the audience.
Writing Biographies and Autobiographies
These are detailed accounts of a person’s life and should be written in an engaging and informative style.
Book Review Writing in Marathi
Provide a critical evaluation of the book, discussing the theme, plot, and quality of writing.
Summarizing Texts in Marathi
A summary should capture the main points of a text concisely and clearly.
[save_as_pdf_pdfcrowd]
Latest Posts
- Step-by-step guide to download and apply for jee mains admit card 202
- Comprehensive 2025 government holidays and recruitment details for job seekers
- JEE Mains Admit Card 2025: Your Step-by-Step Guide to Downloading the Hall Ticket
- Everything You Need to Know About 2025 Government Holidays Recruitment
- Comprehensive Guide to rrb d group recruitment 2025 – Eligibility, Vacancies, and Application
- Detailed guide to nps trust recruitment 2025 vacancies, eligibility and apply process
- Comprehensive guide to hpcl recruitment 2025 notification, vacancies, and application process
- ignou bed admission 2025 complete recruitment guide with eligibility and process
- Comprehensive Guide to Indian Army Agniveer Recruitment 2025 Notification and Jobs
- Everything You Must Know About CBSE Board Exams 2025 Changes & New Rules